Hacking Your Genes: A Guide to Nutrigenomics and How Food Rewrites Your Health Destiny
Byline: Athalon | October 3, 2025
In a previous blog we explored epigenetics revealed a groundbreaking truth: we are not prisoners of our DNA. Our lifestyle choices can act as "software updates" to our genetic hardware, influencing how our genes are expressed. Now, we take the next logical step and explore the single most powerful tool you have for writing that code: your food.
Welcome to the revolutionary world of Nutrigenomics. This cutting-edge science goes beyond calories and macros to reveal that food is, quite literally, a form of biological information. The nutrients you consume are chemical messengers that "talk" to your genes, turning them on or off in ways that can either build resilience and health or pave the way for disease.
If you've ever wondered why some people thrive on a certain diet while others don't, or how you can proactively influence your genetic predispositions, you're in the right place. This guide will unpack the science of how specific foods can become your most powerful tool for a longer, healthier life.
Beyond Calories: Food as Genetic Information
The Science of Nutrigenomics
The central premise of nutrigenomics is that nutrients don't just provide energy; they orchestrate a complex symphony within our cells. Two of the most important epigenetic mechanisms they influence are DNA methylation and histone modification.
DNA Methylation: Think of this as applying a "silencer" to a gene. Certain nutrients, known as methyl donors, provide tiny chemical tags (methyl groups) that attach to a gene and effectively switch it off. This is a crucial process for silencing undesirable genes, such as those that promote inflammation or tumor growth. The most famous methyl donors come from our diet, particularly B vitamins.
Histone Modification: If DNA is the script, histones are the spools it's wound around. How tightly the DNA is wound determines whether a gene can be read. Nutrients can influence enzymes that either tighten the spool (silencing the gene) or loosen it (expressing the gene).
This means your daily meals are actively participating in your genetic expression. The quality of these "instructions" matters immensely. Accurately monitoring your intake of these key micronutrients can be challenging, which is why utilizing a high-quality nutrition tracking app that focuses on micronutrients can be an invaluable tool for anyone serious about this approach.
The Master Switches: Key Nutrients and Their Genetic Roles
While a balanced diet is key, certain "superstar" nutrients have a remarkably powerful and direct effect on our epigenome.
Sulforaphane (from Cruciferous Vegetables): This is one of the most potent nutrigenomic compounds ever discovered. Found abundantly in broccoli sprouts, sulforaphane is a powerful histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor. HDACs are enzymes that keep DNA tightly wound, silencing protective genes. By inhibiting them, sulforaphane helps to turn on powerful anti-cancer and antioxidant genes, like Nrf2, the body's master antioxidant switch.
Folate and B Vitamins (from Leafy Greens, Legumes, Asparagus): These are the workhorses of DNA methylation. Folate (Vitamin B9), B6, and B12 are essential for providing the methyl groups needed to silence pro-inflammatory and disease-promoting genes. A diet rich in these nutrients literally helps you maintain a healthy genetic "off" switch.
Polyphenols (from Berries, Green Tea, Dark Chocolate): This massive class of plant compounds, including resveratrol from grapes and EGCG from green tea, has a broad and beneficial epigenetic influence. They can influence DNA methylation patterns and help regulate genes involved in inflammation, cell growth, and metabolism.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (from Fatty Fish): Beyond their well-known anti-inflammatory benefits, Omega-3s (specifically EPA and DHA) work at the genetic level. They can help down-regulate the expression of inflammatory genes like NF-κB, thereby reducing the root cause of many chronic diseases.
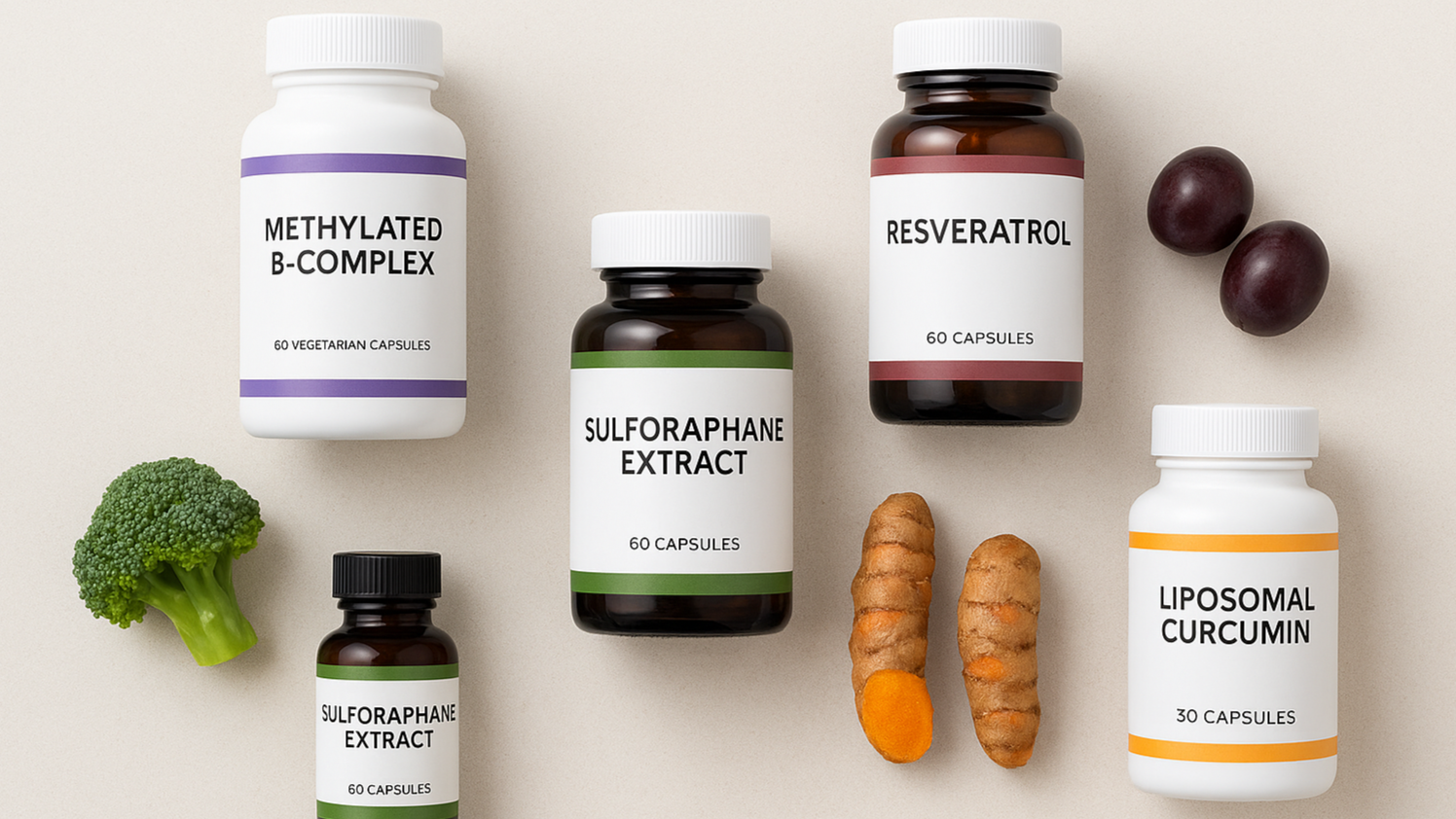
Strategic Supplements to Amplify Your Genetic Potential
While a whole-food diet is the foundation, strategic supplementation can ensure you're providing your body with an optimal dose of these gene-influencing compounds.
Methylated B-Complex: For Optimal Methylation
Many people have genetic variations (like MTHFR) that impair their ability to convert standard B vitamins into their active forms. A bioactive methylated B-complex containing methylfolate (L-5-MTHF) instead of folic acid, and methylcobalamin (B12), ensures your body has the ready-to-use methyl donors it needs to maintain a healthy epigenome.
Sulforaphane Extract: The Potent Gene Activator
While broccoli sprouts are a fantastic food source, achieving a consistent, therapeutic dose of sulforaphane daily can be difficult. A high-quality, stabilized sulforaphane extract from broccoli sprouts provides a concentrated and reliable way to activate the powerful Nrf2 pathway.
Resveratrol: For Longevity Gene Support
Resveratrol is a potent polyphenol famous for its ability to activate sirtuins, a class of proteins often called "longevity genes" for their role in cellular repair and stress resistance. To get a meaningful dose, a high-purity trans-resveratrol supplement can provide targeted support for these anti-aging pathways.
Curcumin: The Master Anti-Inflammatory
The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, is a potent anti-inflammatory that exerts some of its effects via epigenetic modulation. It can influence both DNA methylation and histone modification. To overcome its poor absorption, a liposomal or black pepper-enhanced curcumin supplement is essential for bioavailability.
The "Epigenetic Plate"
Aim for this balance at most meals:
50% Colorful Vegetables: Maximize your intake of polyphenols, vitamins, and fiber.
25% Clean Protein: Provides amino acids, the building blocks for enzymes and cellular machinery.
25% Healthy Fats & Fiber-Rich Carbs: Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil, nuts) and fiber support a healthy gut microbiome, which also influences epigenetics.
Top 5 "Gene-Hacking" Foods to Add This Week:
Broccoli Sprouts: Add them to salads and smoothies for a sulforaphane boost.
Wild-Caught Salmon: Aim for two servings a week for a potent dose of Omega-3s.
Dark Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale): The cornerstone of any methylation-supportive diet.
Blueberries: A delicious source of brain-protective polyphenols.
Matcha Green Tea: Provides a concentrated dose of the powerful polyphenol EGCG.
Making a daily "epigenetic smoothie" with leafy greens, berries, and healthy fats using a high-powered blender is an incredibly efficient way to start your day with gene-supportive nutrients.
Conclusion: You Are the Author of Your Health Story
Nutrigenomics is one of the most empowering fields in modern science. It unequivocally shows that we are active participants in our health, not passive victims of our genetic inheritance. Your fork is a far more powerful tool than you ever imagined. Every meal is an opportunity to provide your body with beneficial instructions, to silence harmful genes, and to express the vibrant, resilient, and healthy person encoded in your DNA.
Disclaimer: Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen or exercise program to ensure it is appropriate for your individual health needs.